Reaction: PM20D1 transforms oleoyl-phe from oleate and phe
- in pathway: Oleoyl-phe metabolism
Extracellular PM20D1 (N-fatty-acyl-amino acid synthase/hydrolase PM20D1) catalyzes the reversible condensation of L-phenylalanine (L-phe) and oleate ((9Z)-octadecenoate) to form oleoyl-phe (N-(9Z-octadecenoyl)-L-phenylalanine) and water. In addition to the condensation of phe with oleate ((9Z)-octadecenoate) annotated here, purified human PM20D1 protein in vitro can catalyze the condensation of leucine and isoleucine with oleate and other long-chain unsaturated fatty acids including arachidonate, with lower efficiencies. Although the reverse (hydrolysis) direction of this reaction is thermodynamically favored, expression of PM20D1 protein in mice or in cultured cells was associated with elevated levels of oleoyl-phe in serum and culture media, respectively. Treatment of cultured mouse brown adipose tissue adipocytes with oleoyl-phe induced uncoupled respiration independently of UCP1 (uncoupling protein 1) and consistent with this observation, expression of PM20D1 and elevated blood levels of oleoyl-phe in mice were associated with increased energy expenditure and improved glucose homeostasis. These results suggest a physiological role for PM20D1 and its condensation reaction product in thermogenesis and raise the possibility that oleoyl-phe and related molecules might have a clinical role in treatment of obesity (Long et al. 2016).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H2O [extracellular region]
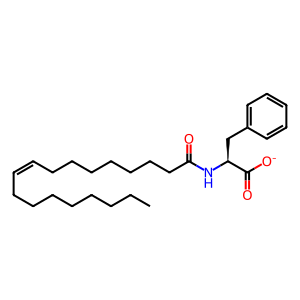
oleoyl-Phe [extracellular region]
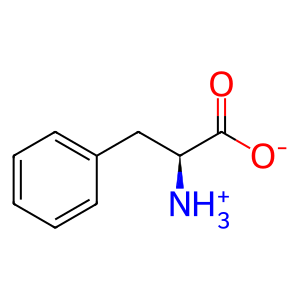
L-Phe [extracellular region]
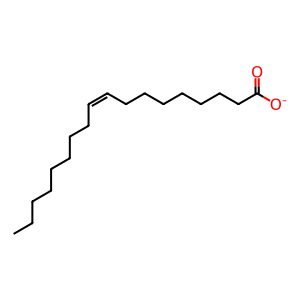
oleate [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9673053
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
L-phenylalanine zwitterion
oleate
Reaction output - small molecules:
water
N-oleoyl-L-phenylalaninate
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9673053