Reaction: O-GlcNAcylation of RIPK3 (TLR4 signaling)
- in pathway: Regulation of necroptotic cell death
Receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 3 (RIPK3) plays an integral role in mediating a pro-inflammatory form of cell death, termed necroptosis. RIPK3-dependent signaling is tightly regulated by post-translational modifications, including proteolysis, phosphorylation and ubiquitylation. O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) transferase (OGT), a key enzyme for protein O-GlcNAcylation, was found to limit RIPK3 kinase-mediated inflammation and necroptosis in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMM) and human monocyte-like THP-1 cells (Li X et al. 2019). Genetic deletion of Ogt in myeloid cells markedly exacerbated cytokine storm and host mortality in experimental sepsis in mice (Li X et al. 2019). Further, impaired O-GlcNAc signaling in patients with liver cirrhosis and in mice with ethanol-induced liver injury exhibited a significant increase in the level of phosphorylated mixed lineage kinase domain-like (MLKL) (Zhang B et al. 2019). OGT utilizes uridine diphosphate (UDP)-GlcNAc to catalyze O-linked attachment of a single GlcNAc to serine or threonine residues in target proteins. Co-immunoprecipitation assay showed that RIPK3 directly interacts with OGT in human embryonic kidney 293T (HEK293T) cells that were transfected with the tagged RIPK3 and OGT proteins (Li X et al. 2019; Zhang B et al. 2019). Further, both RIPK3 O-GlcNAcylation and the association between RIPK3 and OGT increased upon LPS stimulation in mouse BMM cells, despite attenuated total protein O-GlcNAcylation, which suggests that OGT actively and specifically promotes RIPK3 O-GlcNAcylation in response to LPS. In addition, upon LPS challenge, Ogt-deficient BMMs produced significantly higher amounts of inflammatory mediators. Similarly, OGT-deficient human THP-1 cells increased cytokine production in response to TLR2 (Pam3Cys), TLR4 (LPS) or TLR9 (CpG) agonists, suggesting that OGT negatively regulates cytokine production both in mouse and human cells (Li X et al. 2019). Thiamet-G (TMG), that increased intracellular O-GlcNAc levels, effectively shortened the half-life of RIPK3 in human non-small cell lung carcinoma cell line derived from the lymph node (H1299) as compared with the vehicle control suggesting that O-GlcNAcylation of RIPK3 decreases its protein stability (Zhang B et al. 2019). Truncations of human RIPK3 in conjunction with mass spectrometry and subsequent site-directed mutagenesis pinpointed the site of O-GlcNAcylation as residue T467 within the RIP homotypic interaction motif (RHIM) domain of RIPK3 (Li X et al. 2019). Examination of a RIPK3 T467A mutant, which is resistant to O-GlcNAc modification, confirmed that this modification repressed LPS-induced RIPK3-mediated phosphorylation events, cytokine production, and necroptotic cell death in THP-1 and RIPK3-expressing HEK293T cells (Li X et al. 2019). It should be noted that T467 on human RIPK3 is only partially conserved among mammalian species, suggesting a possibility that additional functional O-GlcNAcylation site(s) could exist in other species (Li X et al. 2019). Further, the O-GlcNAcylation of RIPK3 diminished RIPK1:RIPK3 and RIPK3:RIPK3 RHIM interactions and downstream RIPK3 kinase activation in RIPK3-expressing HEK293T cells. These findings are supported by structural modeling showing that O-GlcNAc modification lies in close proximity to the conserved RHIM VQVG motif and likely perturbs RHIM-mediated protein interaction through steric hinderance. Collectively these data show that OGT targets residue T467 of RIPK3 for O-GlcNAcylation to prevent RIPK3 activation in human cells. These findings demonstrate an immuno-metabolic crosstalk linking the hexosamine biosynthesis pathway (HBP)-associated O-GlcNAc signaling and innate immune cell activation (Li X et al. 2019; Zhang B et al. 2019).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
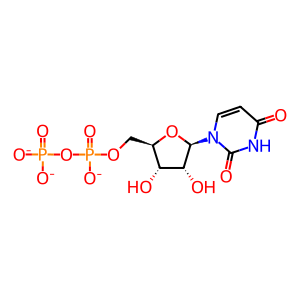
UDP [cytosol]
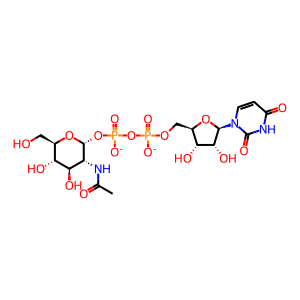
UDP-GlcNAc [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9687828
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine(2-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
UDP(3-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9687828