Reaction: Spike protein gets palmitoylated
- in pathway: Maturation of spike protein
Palmitoylation of SARS-CoV-2 Spike can occur on multiple different cysteine residues in the S2 endodomain; however, palmitoylation appears to occur more efficiently on the N-terminal endodomain cysteines. Inhibition of palmitoylation reduced the proteolytic processing of the full (S1+S2 precursor) Spike protein (Nguyen et al, 2020). Treatment with a protein palmitoylation inhibitor suppresses S-mediated membrane fusion and the entry of SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus into host cells. In a Spike mutant lacking Cys residues at the C-terminus the palmitoylation was completely abolished, with a decrease of S-trimer formation. The host proteins ZDHHC5 and GOLGA7 were found to enhance SARS-CoV-2 S protein palmitoylation synergistically, so the involvement of the ZDHHC5:GOLGA7 palmitoyltransferase complex in SARS-CoV-2 Spike palmitoylation seems likely (Wu ZC et al, 2021; Zeng et al, 2021; Nguyen et al, 2020; Lee et al, 2020). Further investigations showed the possible participation of other host palmitoylation complexes acting on different sites in the Spike protein (Mesquita et al, 2021; Puthenveetil et al, 2021; Li DQ et al, 2022). We included palmitoyltransferases in the annotation that had the support of at least two papers.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
CoA-SH [endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment]
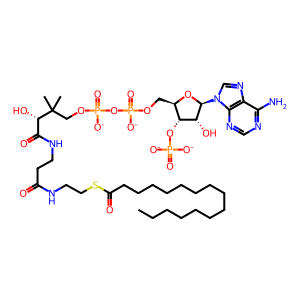
palmitoyl-CoA [endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9694341
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
palmitoyl-CoA(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
coenzyme A(4-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9694341