Reaction: RTC completes synthesis of the minus strand genomic RNA complement
- in pathway: Replication of the SARS-CoV-2 genome
This COVID-19 event has been created by a combination of computational inference (see https://reactome.org/documentation/inferred-events) from SARS-CoV-1 data and manual curation, as described in the summation for the overall SARS-CoV-2 infection pathway.
The replication-transcription complex (RTC) completes synthesis of the genomic RNA complement (minus strand). The complex of nsp7 and nsp8 confers processivity to nsp12, the virally encoded RNA-dependent RNA polymerase that replicates the viral genomic RNA, enabling the RTC to complete the RNA synthesis with a very low dissociation rate. nsp7 plays a crucial role in maintaining binding of the RTC to the RNA. nsp14 subunit of the RTC does not affect the processivity (Subissi et al. 2014).
The replication-transcription complex (RTC) completes synthesis of the genomic RNA complement (minus strand). The complex of nsp7 and nsp8 confers processivity to nsp12, the virally encoded RNA-dependent RNA polymerase that replicates the viral genomic RNA, enabling the RTC to complete the RNA synthesis with a very low dissociation rate. nsp7 plays a crucial role in maintaining binding of the RTC to the RNA. nsp14 subunit of the RTC does not affect the processivity (Subissi et al. 2014).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
PPi [cytosol]
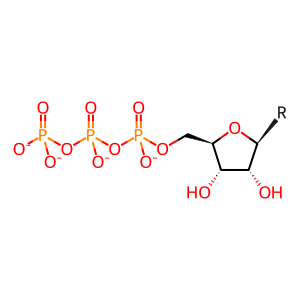
NTP(4-) [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9694549
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
nucleoside 5'-triphoshate(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
diphosphate(3-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9694549