Reaction: nsp12 synthesizes minus strand SARS-CoV-2 genomic RNA complement
- in pathway: Replication of the SARS-CoV-2 genome
Virally encoded RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (nsp12, also known as RdRP) is the key component of the replication transcription complex (RTC). SARS-CoV-2-derived nsp12, in complex with nsp7 and nsp8, was shown to have RNA polymerization activity on a poly-U template (Yin et al. 2020). Details of SARS-CoV-2 replication have not yet been elucidated and are inferred from SARS-CoV-1. As SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV-1 are plus strand RNA viruses, nsp12 first synthesizes the complementary minus RNA strand. The purified SARS-CoV-1 nsp12 shows both primer dependent and primer-independent RNA synthesis activities using homopolymeric RNA templates. The catalytic activity of nsp12 is strictly dependent on manganese ions (Mn2+) and primers when the template is a viral-genome-derived RNA representing part of the 3’-UTR of the plus strand with a polyA tail. A 36 nucleotide sequence from the 3’-UTR, predicted to form a stable stem-loop structure, seems to be the minimal cis-acting RNA element required for nsp12 to initiate RNA synthesis (Ahn et al. 2012). The complex of nsp7 and nsp8 confers processivity to nsp12 (Subissi et al. 2014).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
PPi [cytosol]
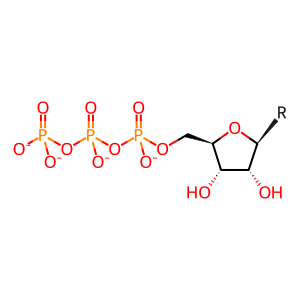
NTP(4-) [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9694605
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
nucleoside 5'-triphoshate(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
diphosphate(3-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9694605