Reaction: GSDME (1-270) binds cardiolipin
- in pathway: Pyroptosis
Gasdermin E (GSDME) is cleaved by caspase 3 (CASP3) at D270 in response to apoptotic stimuli (Rogers C et al. 2017; Wang Y et al. 2017). The released N‑terminal fragment of GSDME (1‑270) targets the plasma membrane to drive pyroptosis in GSDME‑expressing cells (Wang Y et al. 2017). In addition, the N‑terminal fragment of mouse GSDME binds to cardiolipin liposomes causing severe leakage (Wang Y et al. 2017). Although cardiolipin is primarily located in the inner mitochondrial membrane, the outer mitochondrial membrane also contains around 10‑20% cardiolipin and cardiolipin translocates in a regulatable manner between the compartments (Liu J et al. 2003; reviewed in Dudek J 2017). Confocal microscopy and biochemical analysis revealed that tagged‑GSDME (1‑270) localized to mitochondria and triggered release of proapoptotic proteins such as cytochrome c (CYCS) upon ectopic expression in human HeLa cells or human embryonic kidney 293T (HEK293T) cells (Rogers C et al. 2019). Endogenous GSDME (1‑270) also localized to the mitochondrial fraction during apoptosis in TNFα plus actinomycin D (TNFα/actD)‑treated human lymphoid CEM‑C7 cells. Apoptotic stimuli‑triggered cleavage of GSDME (1‑270) induced CYCS release and ROS production in CEM‑C7 cells (Rogers C et al. 2019). These data suggest that the N‑terminal fragment of GSDME (1‑270) can permeabilize the mitochondria in response to apoptotic stimuli (Rogers C et al. 2019), however, the physiological relevance of this event remains to be determined.
This Reactome event describes the GSDME (1‑275) binding to mitochondrial cardiolipin leading to CYCS release from the mitochondria.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
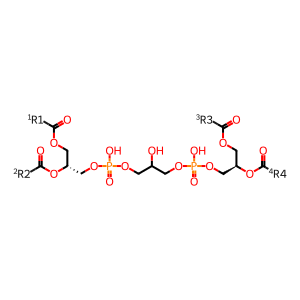
cardiolipin [mitochondrial outer membrane]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9710354
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
cardiolipin
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9710354