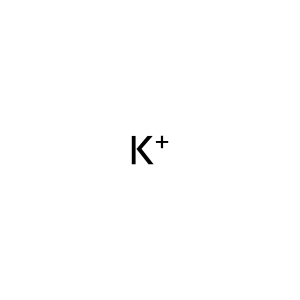Reaction: ATP4A:ATP4B exchanges K+ for H+
- in pathway: Ion transport by P-type ATPases
The potassium-transporting ATPase heterodimer comprising a catalytic alpha and stabilising beta chain (ATP4A:ATP4B), catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of H+ and K+ ions across the plasma membrane. The human gene ATP4A encodes the catalytic alpha subunit (Maeda et al. 1990). One human gene encodes the beta subunit, ATP4B (Ma et al. 1991). ATP4A is responsible for acid production in the stomach.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [extracellular region]
K+ [cytosol]
Pi [cytosol]
ADP [cytosol]
K+ [extracellular region]
H2O [cytosol]
H+ [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9727198
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
potassium(1+)
water
hydron
ATP(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
potassium(1+)
hydrogenphosphate
ADP(3-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9727198