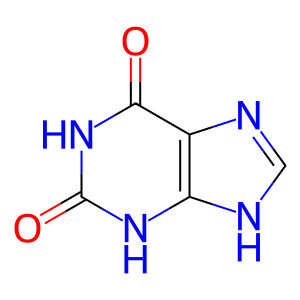
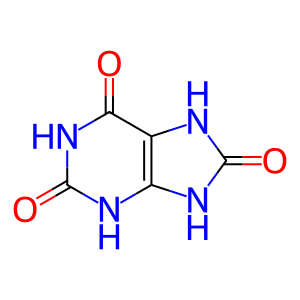
Reaction: XDH dehydrogenates xanthine to form urate
- in pathway: Purine catabolism
Cytosolic xanthine dehydrogenase (XDH) in its dehydrogenase form catalyzes the reaction of xanthine with H2O and NAD+ to form urate and NADH + H+. The active form of the enzyme is a dimer (Saksela and Raivio 1996; Yamaguchi et al. 2007). The enzyme can be converted to an oxidase form that catalyzes the reaction of xanthine with O2 to form urate and H2O2 (Ichida et al. 2012), annotated separately.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [cytosol]
urate [cytosol]
NADH [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
XAN [cytosol]
NAD+ [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9727349
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
9H-xanthine
NAD(1-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
7,9-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6,8(3H)-trione
NADH(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9727349