Reaction: IMPDH tetramers dehydrogenate 6TIMP to 6TXMP
- in pathway: Azathioprine ADME
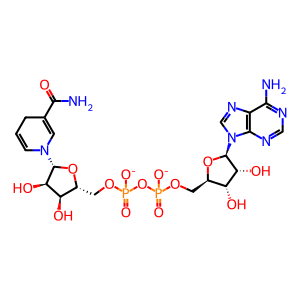
Inosine 5′-monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) is a key enzyme in the de novo synthesis of guanine nucleotides and is positioned at the branch point between adenine and guanine biosynthesis. It is also strategically positioned in the metabolic pathway of thiopurines. IMPDH is considered to be the rate-limiting enzyme in the metabolism of thiopurine drugs to 6-thioguanine nucleotides (6-TGNs) (Leyva et al. 1976). IMPDH dehydrogenates 6-thioinosine 5’-monophosphate (6TIMP) to 6-thioxanthosine 5'-monophosphate (6TXMP), an intermediate metabolite in the formation of 6-TGNs.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
6TXMP [cytosol]
H+ [cytosol]
NADH [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
6TIMP [cytosol]
NAD+ [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9748945
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
6-Thioinosine-5'-monophosphate(2-)
NAD(1-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
6-Thioxanthine 5'-monophosphate(2-)
hydron
NADH(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9748945