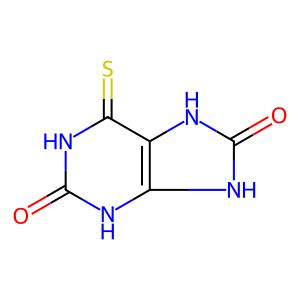
Reaction: XDH oxidises 6MP to 6TU
- in pathway: Azathioprine ADME
6-mercaptopurine (6MP) can be metabolized via three competing pathways; oxidation by xanthine oxidase (XDH), methylation by thiopurine methyl S-transferase (TPMT) and conversion by hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HPRT1).
6-mercaptopurine (6MP) is subjected to high first-pass metabolism due to oxidation in intestinal cells and liver cells by xanthine oxidase (XDH) (Saksela & Raivio 1996, Yamaguchi et al. 2007, Choughule et al. 2014). This reaction produces an inactive metabolite 6-thiouric acid (6TU, via 8-OH-6MP), which is excreted in urine. Patients with low XDH expression can exhibit elevated levels of the toxic antimetabolite 6MP which might result in a higher risk of thiopurine-induced adverse effects (Ding et al. 2021).
6-mercaptopurine (6MP) is subjected to high first-pass metabolism due to oxidation in intestinal cells and liver cells by xanthine oxidase (XDH) (Saksela & Raivio 1996, Yamaguchi et al. 2007, Choughule et al. 2014). This reaction produces an inactive metabolite 6-thiouric acid (6TU, via 8-OH-6MP), which is excreted in urine. Patients with low XDH expression can exhibit elevated levels of the toxic antimetabolite 6MP which might result in a higher risk of thiopurine-induced adverse effects (Ding et al. 2021).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [cytosol]
6TU [cytosol]
NADH [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
NAD+ [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9748991
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
NAD(1-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
6-Thiourate
NADH(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9748991