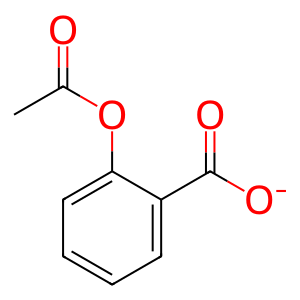
Reaction: SLCO2B1-1 transports ASA- from extracellular region to cytosol of GI cells
- in pathway: Aspirin ADME
Higher uptake of dissolved acetylsalicylate (ASA-) versus neutral acid shows there are transmembrane transport processes specific to ASA- or similar ions (Leonards, 1963). For salicylate, experiments with monolayers of Caco-2 cells have shown a mixture of pH-dependent passive and active influx, and one of the participating transport proteins is SLCO2B1 (formerly OATP-B). SLCO2B1 isoform 1 is the form expressed in the small intestine (Neuhoff et al, 2005; Koljonen et al, 2008). Based on this observation, it is likely that SLCO2B1 also transports ASA-.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
ASA- (GI cell) [cytosol]
ASA- [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9749607
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
acetylsalicylate
Reaction output - small molecules:
acetylsalicylate
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9749607