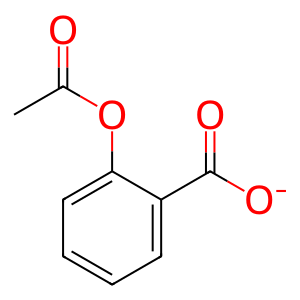
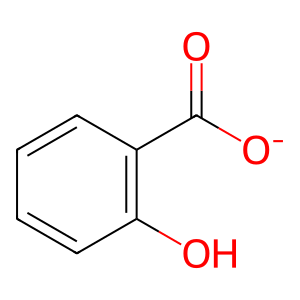
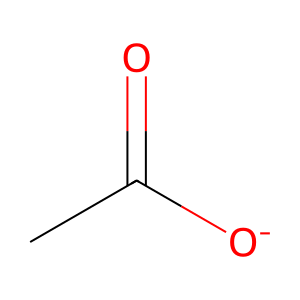
Reaction: BCHE hydrolyzes ASA-
- in pathway: Aspirin ADME
Acetylsalicylate (ASA-) is hydrolyzed by two plasma esterases. About 80% of aspirin esterase activity in the blood is due to the erythrocyte enzyme butyrylcholine esterase (pseudocholinesterase, BCHE). BCHE hydrolyzes acetylsalicylate (ASA-), producing acetate and salicylate (Rainsford et al, 1980; Costello & Green, 1983).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [extracellular region]
ST [extracellular region]
acetate [extracellular region]
H2O [extracellular region]
ASA- [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9749609
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
acetylsalicylate
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
salicylate
acetate
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9749609