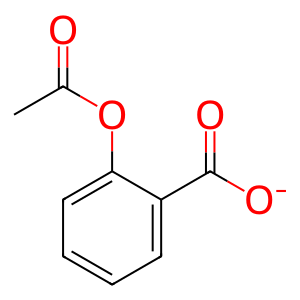
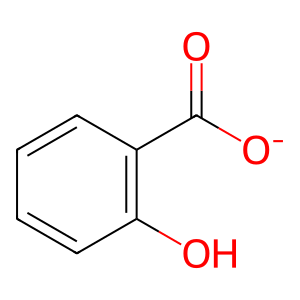
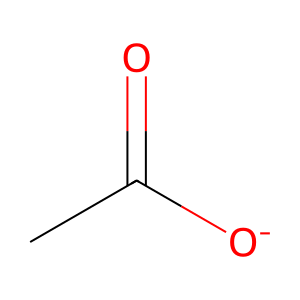
Reaction: CES1,CES2 hydrolyze ASA- to ST
- in pathway: Aspirin ADME
CES1 and CES2 hydrolyze acetylsalicylate (ASA-) in hepatic cells. Although ASA- is also hydrolyzed to salicylate (ST) without enzymatic assistance, this process is rather slow (Rowland et al, 1972; Dressman et al, 2012). In gastrointestinal mucosa cells the predominant esterase is carboxylesterase 2 (CES2) (Imai et al, 2006), and in liver it has significant activity. In liver the main aspirin esterase is CES1, with minor presence of CES2 (Inoue et al, 1980; Imai et al, 2006; Schwer et al, 1997). Both enzymes hydrolyze ASA-, producing acetate and ST (Tang et al, 2006; Imai, 2006; Lian et al, 2017).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
ST (hepatocyte) [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
acetate [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
H2O [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
ASA- (hepatocyte) [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9749792
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
acetylsalicylate
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
salicylate
acetate
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9749792