Reaction: ACY1:Zn2+ dimer deacetylates NAC to L-Cys
- in pathway: Paracetamol ADME
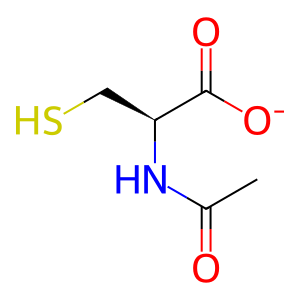
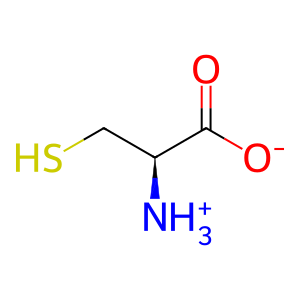
The effects of paracetamol (APAP) poisoning can be reversed by administration of N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) within 15hrs of APAP intake. This treatment is effective in preventing liver damage, hepatic failure, renal damage, and death (Prescott et al. 1977, Prescott 1981). NAC provides L-cysteine (L-Cys) for the formation of the tripeptide glutathione, which can conjugate the reactive APAP metabolite N-acetyl-p-benzoquinine imine (NAPQI), thereby reducing damage. NAC is thought to be deacetylated to L-Cys by aminocylase 1 (ACY1), a dimeric enzyme highly expressed in the kidneys (Stocker et al. 2012, review Pedre et al. 2021).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
L-Cys [cytosol]
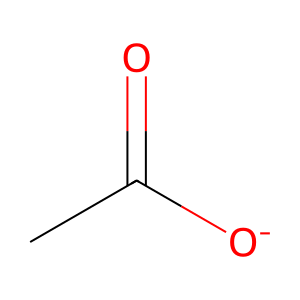
acetate [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
NAC [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9753944
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
N-acetyl-L-cysteinate
Reaction output - small molecules:
L-cysteine zwitterion
acetate
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9753944