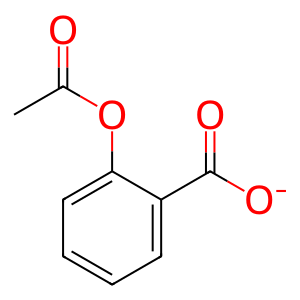
Reaction: Acetylsalicylic acid dissolves
- in pathway: Aspirin ADME
Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) is classified as "highly soluble", meaning that the highest therapeutically used single dose (1000 mg) dissolves in 250 ml of water to its ionized form acetylsalicylate (ASA-). ASA- in solution has an increased rate of uptake versus aspirin in tablet form and poses fewer risks to the stomach (Leonards, 1963; Dressman et al, 2012).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [extracellular region]
H2O [extracellular region]
ASA- [extracellular region]
H2O [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9757434
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
water
acetylsalicylate
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9757434