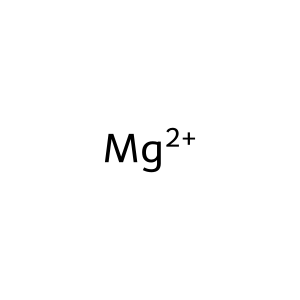Reaction: E1 mediated ubiquitin activation
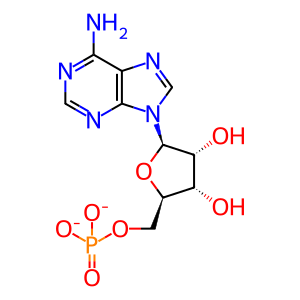
Ubiquitin is activated in an ATP-dependent manner, catalyzed by E1 ubiquitin-activating enzymes. In the first step of ubiquitin activation, the E1 enzyme binds ATP, Mg+2 and ubiquitin, and catalyses ubiquitin C-terminal acyl-adenylation (Ubiquitin-AMP). In the second step, the catalytic cystine in the E1 attacks the ubiquitin-adenylate (Ub-AMP) to form the activated ubiquitin-E1 thioester-bonded complex and an AMP leaving group. The intermediate reaction involving the formation of the ubiquitin-AMP complex is not represented here.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
PPi [cytosol]
Mg2+ [cytosol]
AMP [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
Mg2+ [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-983153
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
ATP(4-)
magnesium(2+)
Reaction output - small molecules:
diphosphate(3-)
magnesium(2+)
adenosine 5'-monophosphate(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-983153