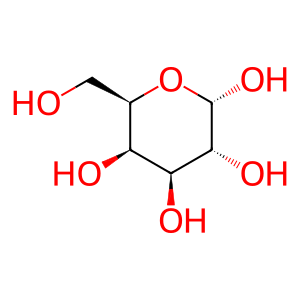
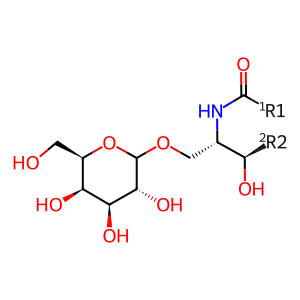
Reaction: GLA hydrolyzes PSAP(195-273):Gal2Cer:PE
- in pathway: Glycosphingolipid catabolism
Alpha-galactosidase A (GLA) (Bishop et al. 1986) removes the terminal galactose residue from glycolipids or glycoproteins, mobilized by PSAP(195-273) (Saposin B), resulting in galactose and an alcohol. An example is the Fabry disease substrate digalactosylceramide (Gal2Cer) which is hydrolysed to form galactose and galactosylceramide (GalCer) (Dean & Sweeley, 1979). GLA functions as a homodimer (Garman & Garboczi 2004) and defects in this enzyme lead to Fabry disease (FD) (MIM:301500), a rare X-linked sphingolipidosis disease where glycolipids such as Gal2Cer accumulate in many tissues (Garman & Garboczi 2004, Eng et al. 1993, Shabeer et al. 2006).
Researchers also observed elevated Gal2Cer in prosaposin deficiency (PSAPD, MIM: 611721) cases, a rare disease with low levels of all saposins. Saposin B (PSAP(195-273)) is an essential cofactor to the reaction (Bradova et al., 1993; Kase et al., 1996)
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Gal [lysosomal lumen]
GalCer [lysosomal lumen]
H2O [lysosomal lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9841189
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
Reaction output - small molecules:
alpha-D-galactose
galactosylceramide
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9841189