Reaction: Insertion of correct bases opposite the lesion by POLH
- in pathway: Translesion Synthesis by POLH
DNA polymerase eta (POLH) correctly incorporates two adenine deoxyribonucleotides (dAMPs) opposite a TT-CPD (thymine-thymine cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer) lesion. POLH can bypass other types of lesions, such as AP sites and cisplatin-induced intrastrand cross-linked gunanines, preferentially incorporating dAMPs and dGMPs opposite the lesion. While POLH is accurate in translesion synthesis (TLS) across thymine dimers, POLH has a low fidelity in TLS across other DNA damage types and when copying undamaged DNA. One of the protective mechanisms against POLH-induced mutagenesis may be that POLH cannot continue chain elongation after an incorrect nucleotide is incorporated (Matsuda et al. 2000, Masutani et al. 2000).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
PPi [nucleoplasm]
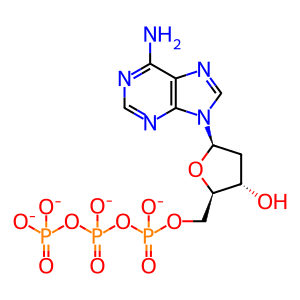
dATP [nucleoplasm]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-110317
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
dATP(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
diphosphate(3-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-110317