Reaction: Oxidative dealkylation of 1-EtA damaged DNA by ABH3
- in pathway: ALKBH3 mediated reversal of alkylation damage
ALKBH3, a homolog of E.coli AlkB (Trewick et al. 2002), removes the ethyl group from 1-ethyladenine (1-etA) in a reaction dependent on alpha-ketoglutarate, oxygen and Fe2+. ALKBH3 directly reverses alkylating damage of DNA in the form of 1-etA, releasing acetaldehyde (Duncan et al. 2002). The reversal of alkylating damage of dsDNA by ALKBH3 requires the presence of DNA helicase ASCC3, a component of the activating signal co-activator complex (Dango et al. 2011). ALKBH3 can also repair methylated RNA (Aas et al. 2003).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
CO2 [nucleoplasm]
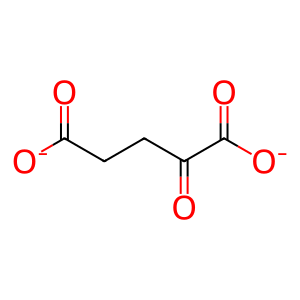
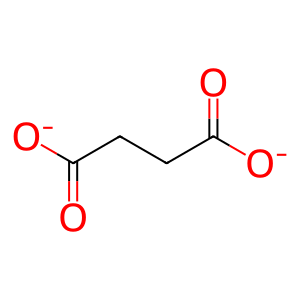
SUCCA [nucleoplasm]
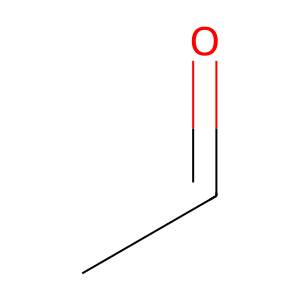
CH3CHO [nucleoplasm]
2OG [nucleoplasm]
O2 [nucleoplasm]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-112125
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
2-oxoglutarate(2-)
dioxygen
Reaction output - small molecules:
carbon dioxide
succinate(2-)
acetaldehyde
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-112125