Reaction: Cytosolic HIF1AN (FIH1) hydroxylates asparagine residues of Hypoxia-inducible Factor Alpha (HIF1A,HIF2A)
- in pathway: Cellular response to hypoxia
HIF1AN (FIH, FIH-1) forms a homodimer that hydroxylates an asparagine residue on HIF1A and HIF2A (Hewitson et al. 2002, Lando et al. 2002, Metzen et al. 2003, Koivunen et al. 2004, Lancaster et al. 2004). The hydroxylation of the asparagine interferes with the interaction between HIF1A/HIF2A and p300, a histone acetylase, and therefore inhibits the ability of HIF1A/2A to activate transcription of target genes (Lando et al. 2002). Because molecular oxygen is a substrate of the reaction, hypoxia is a negative regulator of this reaction and thereby increases transcriptional activation of target genes by HIF1A/2A.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
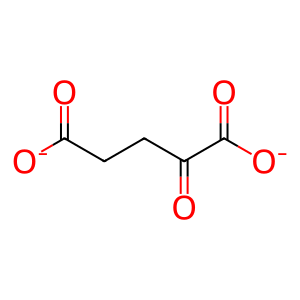
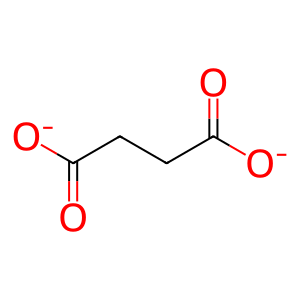
SUCCA [cytosol]
CO2 [cytosol]
2OG [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-1234164
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
2-oxoglutarate(2-)
dioxygen
Reaction output - small molecules:
succinate(2-)
carbon dioxide
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-1234164