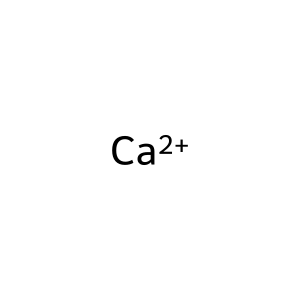Reaction: P2X1-mediated entry of Ca++ from plasma
- in pathway: Elevation of cytosolic Ca2+ levels
The P2X1 receptor is a rapidly-desensitized ATP-gated cation channel with relatively high calcium permeability. It has highest expression in smooth muscle and platelets. P2X1 receptor activation cannot induce platelet aggregation but does contribute to aggregation seen in response to collagen (Oury et al. 2001; Hechler et al. 2003). The role of P2X1 is more significant under flow conditions characterized by high shear stress (Hechler et al. 2003; Oury et al. 2004). P2X1 knockout mice havereduced incidence of thrombosis of mesenteric arterioles triggered by laser-induced vessel wall injury and are resistant to the acute systemic thromboembolism induced by infusion of a mixture of collagen and adrenaline (Hechler et al. 2003). Conversely, increased systemic thrombosis has been reported in mice overexpressing the human P2X1 receptor (Oury et al. 2003). P2X1 binding to ATP mediates synaptic transmission between neurons and from neurons to smooth muscle, controlling sympathetic vasoconstriction in small arteries, arterioles and vas deferens.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Ca2+ [cytosol]
Ca2+ [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-139855
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
calcium(2+)
Reaction output - small molecules:
calcium(2+)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-139855