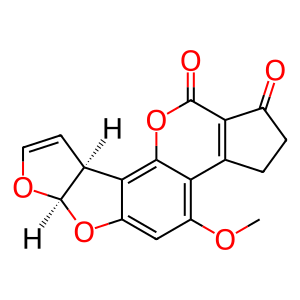
Reaction: CYP1A2,3A4,3A5,2A13 oxidise AFB1 to AFXBO
- in pathway: Aflatoxin activation and detoxification
Aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) requires microsomal oxidation to produce epoxides which cause the toxic and carcinogenic effects. In humans, cytochrome P450 enzymes produce epoxide stereoisomers of AFB1, the most potent being aflatoxin exo-8,9-oxide (AFXBO). This conversion is carried out by at least four P450s; 1A2, 3A4, 3A5 and 2A13. CYP3A4 mainly produces the exo form whereas CYP1A2 produces a racemic mixture of exo and endo forms (Gallagher et al. 1996, He et al. 2006).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H2O [cytosol]
AFXBO [cytosol]
NADP+ [cytosol]
H+ [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
AFB1 [cytosol]
NADPH [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-156526
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
hydron
dioxygen
aflatoxin B1
NADPH(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
water
aflatoxin B1 exo-8,9-epoxide
NADP(3-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-156526