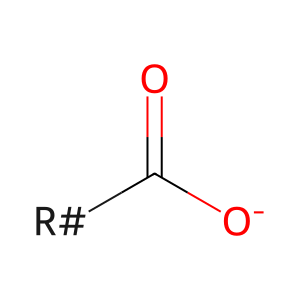
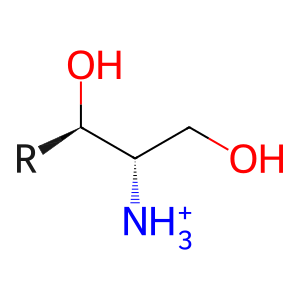
Reaction: ASAH1 hydrolyzes ceramide
- in pathway: Glycosphingolipid catabolism
Acid ceramidase (ASAH1) is a lysosomal enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of ceramide to sphingosine and free fatty acid. It functions as a heterodimer of one alpha and one beta subunit (Bernardo et al. 1995; Gebai et al, 2018). The reaction is stimulated by Saposin D (Sap D, PSAP(405-486)) (Tatti et al, 1999). Defects in ASAH1 are the cause of Farber lipogranulomatosis (FL) (MIM:228000), also called Farber disease (FD) (Zhang et al. 2000, Koch et al. 1996).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
RCOO- [lysosomal lumen]
SPG [lysosomal lumen]
H2O [lysosomal lumen]
CERA [lysosomal lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-1606602
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
N-acylsphingoid
Reaction output - small molecules:
fatty acid anion
sphingoid base(1+)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-1606602