Reaction: Formation of C-strand Okazaki fragments
- in pathway: Processive synthesis on the C-strand of the telomere
After RFC initiates the assembly of the primer recognition complex, the complex of pol delta and PCNA is responsible for incorporating the additional nucleotides prior to the position of the next downstream initiator RNA primer. On the lagging strand, short discontinuous segments of DNA, called Okazaki fragments, are synthesized on RNA primers. The average length of the Okazaki fragments is 100 nucleotides. Polymerase switching is a key event that allows the processive synthesis of DNA by the pol delta and PCNA complex (Lee and Hurwitz 1990, Tsurimoto and Stillman 1991, Nethanel et al. 1992, Brown and Campbell 1993, Waga et al.1994, Bambara et al. 1997). PCNA increases the processivity of the DNA polymerase delta during telomeric C-strand synthesis in a human telomere replication model, but it does not eliminate the DNA polymerase delta stalling on the G-rich template (Lormand et al. 2013).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
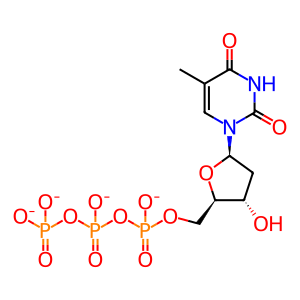
dTTP [nucleoplasm]
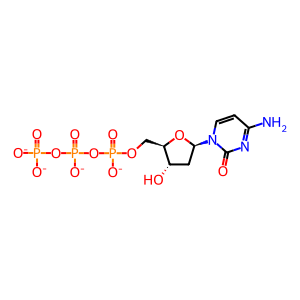
dCTP [nucleoplasm]
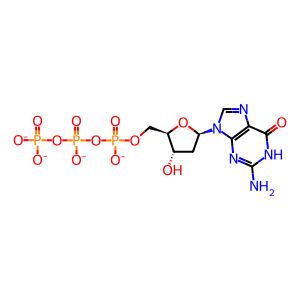
dGTP [nucleoplasm]
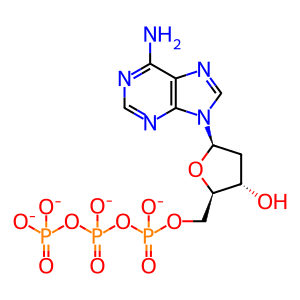
dATP [nucleoplasm]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-174444
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
dTTP(4-)
dCTP(4-)
dGTP(4-)
dATP(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-174444