Reaction: ALAS condenses SUCC-CoA and Gly to form dALA
- in pathway: Heme biosynthesis
The committed step for porphyrin synthesis is the formation of 5-aminolevulinate (ALA) by condensation of glycine (from the general amino acid pool) and succinyl-CoA (from the TCA cycle), in the mitochondrial matrix. The reaction is catalyzed by two different ALA synthases, one expressed ubiquitously (ALAS1) and the other only expressed in erythroid precursors (ALAS2). Both enzymes are expressed as homodimers and require pyridoxal 5-phosphate as a cofactor.
No disease-causing mutations of ALAS1 have been recognised in humans. Mutations in ALAS2 cause X-linked sideroblastic anaemia (XLSA), characterised by a microcytic hypochromic anaemia.
No disease-causing mutations of ALAS1 have been recognised in humans. Mutations in ALAS2 cause X-linked sideroblastic anaemia (XLSA), characterised by a microcytic hypochromic anaemia.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
CoA-SH [mitochondrial matrix]
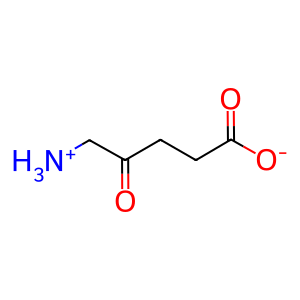
dALA [mitochondrial matrix]
CO2 [mitochondrial matrix]
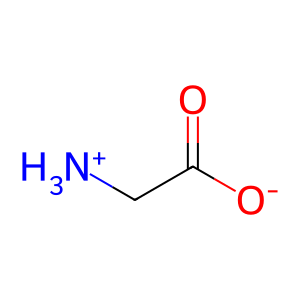
Gly [mitochondrial matrix]
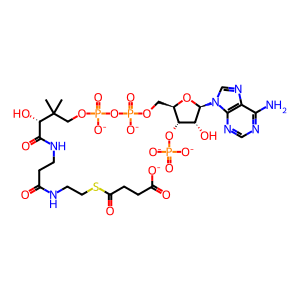
SUCC-CoA [mitochondrial matrix]
H+ [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-189442
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
glycine zwitterion
succinyl-CoA(5-)
hydron
Reaction output - small molecules:
coenzyme A(4-)
5-ammoniolevulinate
carbon dioxide
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-189442