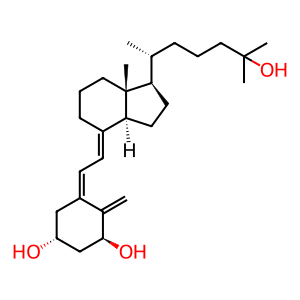
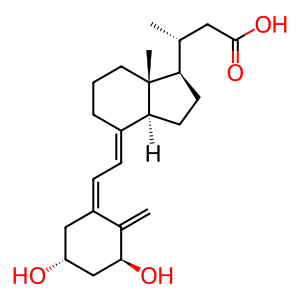
Reaction: CYP24A1 hydroxylates 1,25(OH)2D, inactivating it
- in pathway: Vitamin D (calciferol) metabolism
1-alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D (1,25(OH)2D) is biologically inactivated through a series of reactions beginning with 24-hydroxylation and is most likely a mechanism of elimination. 24-Hydroxylation of vitamin D metabolites is largely regulated inversely to 1-hydroxylation, the initial step towards activation. Human cDNA encoding CYP24A1 was isolated in 1993 (Chen et al. 1993). Studies with expressed human CYP24A1 in Sf21 insect cells indicated that the enzyme could catalyze most, if not all, of the steps in the C23 and C24 oxidation pathways of 25(OH)D and 1,25(OH)2D metabolism (Beckman et al. 1996). Sakaki et al observed that the ratio of initial hydroxylation products at C24 to C23 was 4:1, indicating that the C24-oxidation pathway predominates in humans (Sakaki et al. 2000).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H2O [cytosol]
CTA [cytosol]
NADP+ [cytosol]
H+ [cytosol]
1,25(OH)2D [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
NADPH [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-209765
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
hydron
calcitriol
dioxygen
NADPH(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
water
calcitroic acid
NADP(3-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-209765