Reaction: Tyrosine is hydroxylated to dopa
- in pathway: Catecholamine biosynthesis
Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) is the first enzyme in catecholamine biosynthesis, as well as being the rate-limiting enzyme in that process. TH requires tetrahydrobiopterin and uses iron as a cofactor in the 3,4-hydroxylation of tyrosine to produce dopa. Four isoforms of TH are expressed in the human brain and all have enzymatic activity (Nagatsu, T, 1989; Lewis, DA et al, 1993).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
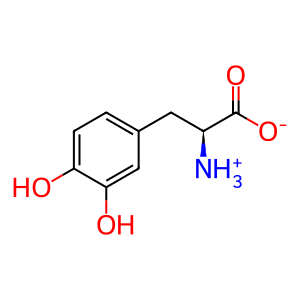
L-Dopa [cytosol]
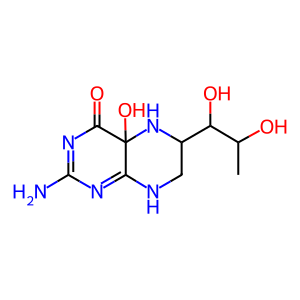
4aOH-BH4 [cytosol]
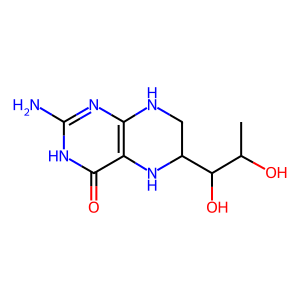
BH4 [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
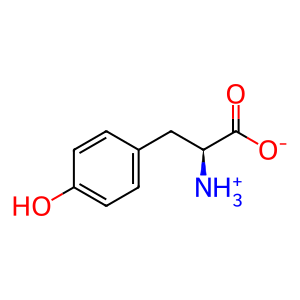
L-Tyr [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-209823
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobiopterin
dioxygen
L-tyrosine zwitterion
Reaction output - small molecules:
L-dopa zwitterion
4a-hydroxytetrahydrobiopterin
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-209823