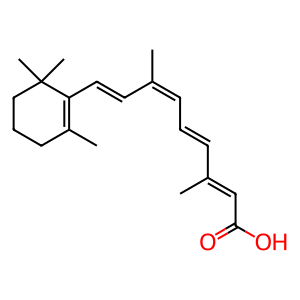
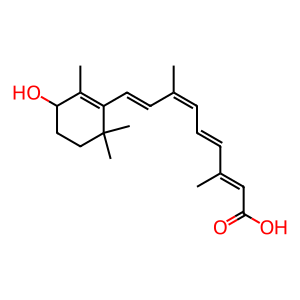
Reaction: CYP26C1 4-hydroxylates 9cRA
- in pathway: Vitamins
Endogenous retinoic acids (RA) which play a role in gene regulation exist as either cis or trans isomers. While CYP26C1 can also hydroxylate the trans form, it is unique in 4-hydroxylating the 9-cis isomer of RA (9cRA) in vitro (Taimi et al. 2004). However, the importance of 9cRA as an endogenous retinoid outside of the pancreas has not been demonstrated.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
4OH-9cRA [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
NADP+ [cytosol]
H+ [cytosol]
9cRA [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
NADPH [cytosol]
4OH-9cRA [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
NADP+ [cytosol]
H+ [cytosol]
9cRA [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
NADPH [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-211923
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
hydron
9-cis-retinoic acid
dioxygen
NADPH(4-)
hydron
9-cis-retinoic acid
dioxygen
NADPH(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
9-cis-4-hydroxyretinoic acid
water
NADP(3-)
9-cis-4-hydroxyretinoic acid
water
NADP(3-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-211923