Reaction: 5S-HETE is oxidised to 5-oxoETE by 5-HEDH
- in pathway: Synthesis of 5-eicosatetraenoic acids
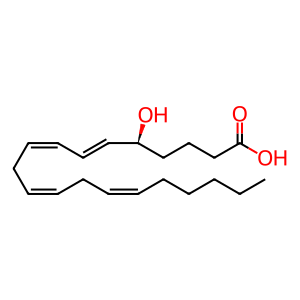
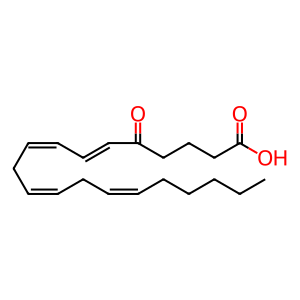
Current literature suggests that 5S-hydroxy-eicosatetraenoic acid (5S-HETE) itself does not appear to play a significant role in biological signalling. However, it can be further oxidised by a 5-hydroxy-eicosatetraenoic acid dehydrogenase (5-HEDH) to form the bioactive 5-oxo-eicosatetraenoic acid (5-oxoETE, also known as 5-KETE. While the gene has not yet been cloned, the biophysical properties of the human enzyme have been well characterised (Powell et al. 1992).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [cytosol]
NADPH [cytosol]
5-oxoETE [cytosol]
5S-HETE [cytosol]
NADP+ [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-2161776
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
5(S)-HETE
NADP(3-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
NADPH(4-)
5-oxo-ETE
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-2161776