Reaction: MII catalyses GDP/GTP exchange on Gt
- in pathway: Activation of the phototransduction cascade
In darkness, the G protein transducin (Gt) is attached to the disk membrane surface with a GDP bound to it and it is inactive. Gt is a heterotrimer of alpha1 (GNAT1) (van Dop et al. 1989, Fong 1992), beta1 (GNB1) (Codina et al. 1986) and gamma1 (GNGT1) (Tao et al. 1993) subunits. Photoactivated rhodopsin (MII or R*) catalyzes the exchange of GTP for GDP bound to Gt. Upon GTP/GDP exchange, Gt is released from MII and the Gt alpha with GTP bound (GNAT1 GTP) dissociates from Gt beta gamma subunits (GNB1:GNGT1). This mechanism was deciphered from bovine experiments (Pugh & Lamb 1993). MII proceeds to activate additional Gt molecules, making this reaction the first amplification step in the phototransduction cascade. A single activated rhodopsin molecule activates tens of Gt molecules. Although phosphorylation of activated rhodopsin (MII) by rhodopsin kinase (GRK1) reduces transducin activation (Khani et al. 1996), complete deactivation occurs only after arrestin (S-antigen or SAG, Yamaki et al. 1988) binds to and sterically caps MII.
Defects in GNAT1 cause the Nougaret type of autosomal dominant, congenital stationary night blindness (Dryja et al. 1996, CSNBAD3; MIM:610444) . Congenital stationary night blindness is a non progressive retinal disorder characterized by impaired night vision.
Defects in GNAT1 cause the Nougaret type of autosomal dominant, congenital stationary night blindness (Dryja et al. 1996, CSNBAD3; MIM:610444) . Congenital stationary night blindness is a non progressive retinal disorder characterized by impaired night vision.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
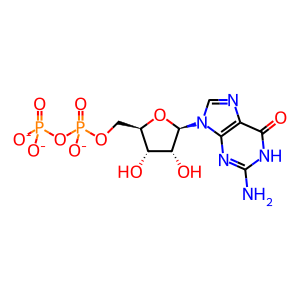
GDP [cytosol]
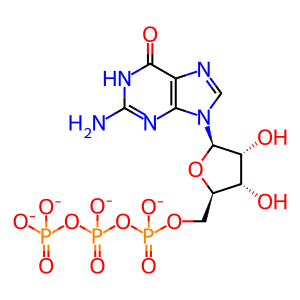
GTP [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-2485180
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
GTP(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
GDP(3-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-2485180