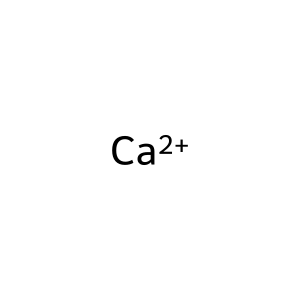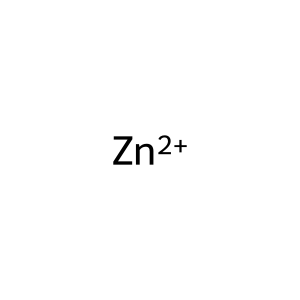Reaction: Exocytosis of Insulin
- in pathway: Regulation of insulin secretion
The major effect of adrenaline and noradrenaline on insulin secretion is the inhibition of exocytosis of pre-existing insulin secretory granules. The inhibition occurs at a "distal site", that is, the effect is most pronounced on granules already near the cytosolic face of the plasma membrane. The effect is caused by the Gi/o alpha:GTP complex but the exact mechanism by which Gi/o alpha:GTP inhibits exocytosis is unknown.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Ca2+ [cytosol]
Ca2+ [extracellular region]
Zn2+ [extracellular region]
Ca2+ [cytosol]
Ca2+ [extracellular region]
Zn2+ [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-265166
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
calcium(2+)
calcium(2+)
Reaction output - small molecules:
calcium(2+)
zinc(2+)
calcium(2+)
zinc(2+)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-265166