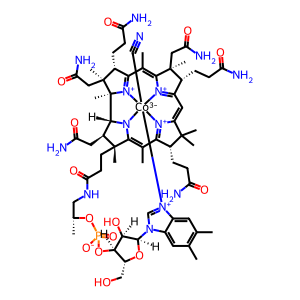
Reaction: MMACHC decyanates CNCbl
- in pathway: Cobalamin (Cbl) metabolism
Cyanocobalamin (CNCbl), a semisynthetic molecule produced from bacterial hydroxocobalamin that is used in many pharmaceuticals and as a food additive, is one of the dietary cobalamins bound successively by TCN1, CBLIF, TCN2 and transported to cells throughout the body (Randaccio et al. 2010). In these cells, CNCbl is reductively decyanated by MMACHC (methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria type C protein) to produce cob(II)alamin (vitamin B12r) and hydrogen cyanide (HCN) (Kim et al. 2008), preparatory to its conversion to active cofactors methylcobalamin and adenosylcobalamin.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
NADP+ [cytosol]
HCN [cytosol]
H+ [cytosol]
NADPH [cytosol]
CNCbl [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-3149519
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
hydron
NADPH(4-)
cyanocob(III)alamin
Reaction output - small molecules:
NADP(3-)
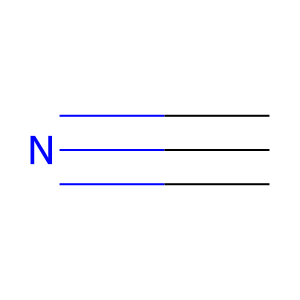
hydrogen cyanide
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-3149519