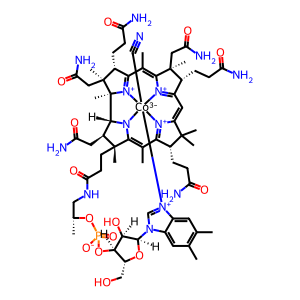
Reaction: Defective MMACHC does not decyanate CNCbl
- in pathway: Defective MMACHC causes MAHCC
Methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria type C protein (MMACHC aka cblC protein) is suggested to be involved in the binding and intracellular transport of cobalamin (Cbl aka vitamin B12, cob(III)alamin). MMACHC can catalyse the removal of the "R" group (formally known as the upper axial ligand) from R-Cbl (where R can be Ado-, Me- or CN-) resulting in the reduction of Cbl (+3 oxidation state) to cob(II)alamin (B12r, vitamin B12r, +2 oxidation state) (Hannibal et al. 2009). Cob(II)alamin is escorted by MMACHC to its destination enzyme partners in the mitochondria and cytosol.
Defects in MMACHC cause methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria type cblC (MMAHCC; MIM:277400). MMAHCC is the most common disorder of cobalamin metabolism and is characterized by decreased levels of the coenzymes adenosylcobalamin (AdoCbl) and methylcobalamin (MeCbl). Affected individuals may have developmental, haematologic, neurologic, metabolic, ophthalmologic, and dermatologic clinical findings (Lerner-Ellis et al. 2006). This disease is usually seen in infancy or childhood but can also present in later life. The common mutations 271dupA (p.R91Kfs*14) and R111*, found in approximately 40% and 5% of patients respectively, and W203* (this mutation is extremely common in Chinese patients where the c.271dupA mutation is virtually unknown) present in early-onset forms of the disease (Morel et al. 2006, Lerner-Ellis et al. 2006, Lerner-Ellis et al. 2009, Liu et al. 2010) whereas the mutations R132* and R161Q present in adulthood (Lerner-Ellis et al. 2009, Liu et al. 2010).
Defects in MMACHC cause methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria type cblC (MMAHCC; MIM:277400). MMAHCC is the most common disorder of cobalamin metabolism and is characterized by decreased levels of the coenzymes adenosylcobalamin (AdoCbl) and methylcobalamin (MeCbl). Affected individuals may have developmental, haematologic, neurologic, metabolic, ophthalmologic, and dermatologic clinical findings (Lerner-Ellis et al. 2006). This disease is usually seen in infancy or childhood but can also present in later life. The common mutations 271dupA (p.R91Kfs*14) and R111*, found in approximately 40% and 5% of patients respectively, and W203* (this mutation is extremely common in Chinese patients where the c.271dupA mutation is virtually unknown) present in early-onset forms of the disease (Morel et al. 2006, Lerner-Ellis et al. 2006, Lerner-Ellis et al. 2009, Liu et al. 2010) whereas the mutations R132* and R161Q present in adulthood (Lerner-Ellis et al. 2009, Liu et al. 2010).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [cytosol]
NADPH [cytosol]
CNCbl [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-3318590
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
hydron
NADPH(4-)
cyanocob(III)alamin
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-3318590