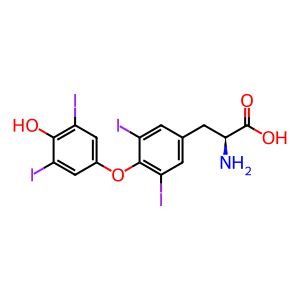
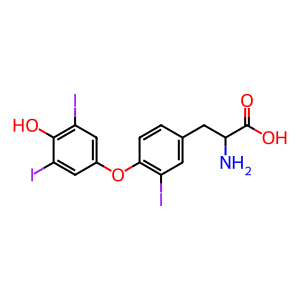
Reaction: Thyroxine is deiodinated to reverse triiodothyronine (RT3)
- in pathway: Regulation of thyroid hormone activity
Type III iodothyronine deiodinase (DIO3) is an integral membrane protein (Baqui M et al, 2003) and catalyzes the conversion of T4 (3,5,3',5'-tetraiodothyronine) into RT3 (3,3',5'-triiodothyronine) and T3 (3,5,3'-triiodothyronine) into T2 (3,3'-diiodothyronine). Both RT3 and T2 are inactive metabolites. It is thought DIO3 plays an essential role for regulation of thyroid hormone inactivation during embryological development.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
I- [cytosol]
T3 [cytosol]
NADP+ [cytosol]
H+ [cytosol]
NADPH [cytosol]
T4 [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-350869
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
hydron
NADPH(4-)
L-thyroxine
Reaction output - small molecules:
iodide
3,3',5'-triiodothyronine
NADP(3-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-350869