Reaction: Nitric Oxide Synthase (NOS) produces Nitric Oxide (NO)
- in pathway: ROS and RNS production in phagocytes
Nitric oxide synthase (NOS) produces NO from L-arginine. There are three isoforms of NOS, endothelial, neuronal and inducible (eNOS, nNOS, and iNOS) (Alderton WK et al. 2001). The three isozymes are regulated differentially. eNOS and nNOS, which are constitutively expressed in certain cells, are activated by he binding of calcium (Ca2+) and calmodulin (Alderton WK et al. 2001; Feng C 2012). iNOS is induced in response to immunostimulatory signals and once synthesized, iNos is constitutively active (Alderton WK et al. 2001; Aktan F 2004; Pautz A et al. 2010). NO produced by NOS acts as a signalling molecule by diffusing across cell membranes to activate soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
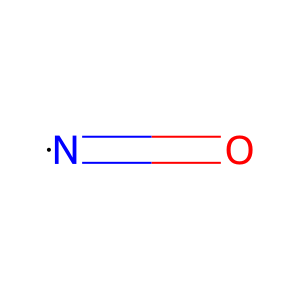
NO [cytosol]
NADP+ [cytosol]
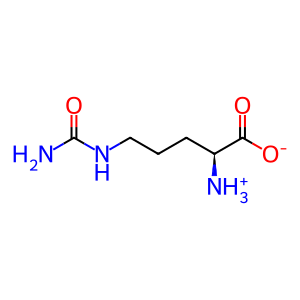
L-Cit [cytosol]
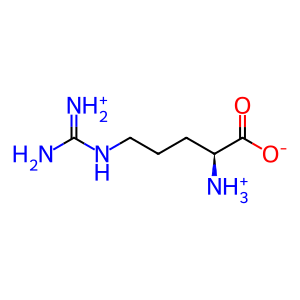
L-Arg [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
NADPH [cytosol]
NO [cytosol]
NADP+ [cytosol]
L-Cit [cytosol]
L-Arg [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
NADPH [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-418436
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
L-argininium(1+)
dioxygen
NADPH(4-)
L-argininium(1+)
dioxygen
NADPH(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
nitric oxide
NADP(3-)
L-citrulline zwitterion
nitric oxide
NADP(3-)
L-citrulline zwitterion
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-418436