Reaction: KDM2A, KDM2B, KDM4A demethylate MeK37-histone H3
- in pathway: HDMs demethylate histones
All characterised lysine demethylases other than KDM1A belong to the jumonji C-domain (JmjC) containing family, members of the Cupin superfamily of mononuclear Fe (II)-dependent oxygenases. They require 2-oxoglutarate (2-OG) and molecular oxygen as co-substrates, producing succinate and carbon dioxide. This hydroxylation-based mechanism does not require a protonatable lysine epsilon-amine group and consequently JmjC-containing demethylases are able to demethylate tri-, di- and monomethylated lyines.
The first reported JmjC-containing demethylases were KDM2A and KDM2B (JHDM1A/B, FBXL11/10). These demethylate lysine-37 of histone H3 when mono- or di-methylated (H3K36Me1/2) (Tsukada et al. 2006). KDM4A (JHDM3A) can demethylate mono-, di and trimethylated lysine-37 of histone H3 (Klose et al. 2006).
The first reported JmjC-containing demethylases were KDM2A and KDM2B (JHDM1A/B, FBXL11/10). These demethylate lysine-37 of histone H3 when mono- or di-methylated (H3K36Me1/2) (Tsukada et al. 2006). KDM4A (JHDM3A) can demethylate mono-, di and trimethylated lysine-37 of histone H3 (Klose et al. 2006).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
CH2O [nucleoplasm]
CO2 [nucleoplasm]
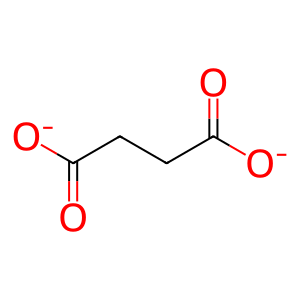
SUCCA [nucleoplasm]
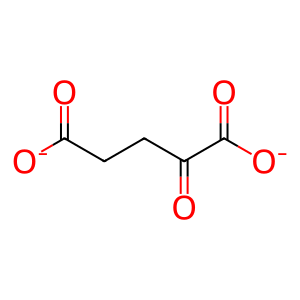
2OG [nucleoplasm]
O2 [nucleoplasm]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-4722133
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
2-oxoglutarate(2-)
dioxygen
Reaction output - small molecules:
formaldehyde
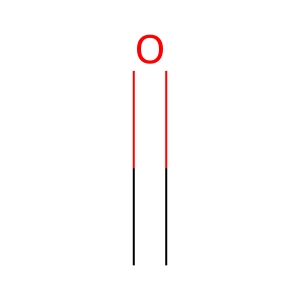
carbon dioxide
succinate(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-4722133