Reaction: a-ketoisocaproate, a-keto-b-methylvalerate, or a-ketoisovalerate + glutamate <=> leu, ile, or val + alpha-ketoglutarate [BCAT2]
- in pathway: Branched-chain amino acid catabolism
Mitochondrial branched-chain-amino-acid aminotransferase (BCAT2) catalyzes the reversible reactions of alpha-ketoisocaproate, alpha-keto-beta-methylvalerate, or a-ketoisovalerate with glutamate to form leucine, isoleucine, or valine, respectively, and alpha-ketoglutarate (Bledsoe et al. 1997). The active enzyme is a homodimer (Yennawar et al. 2001, 2002). In the body, this enzyme is widely expressed but is especially abundant in muscle tissue.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
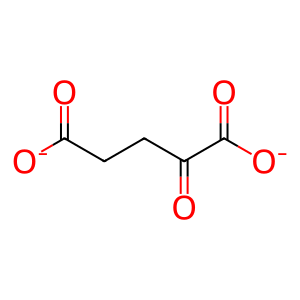
2OG [mitochondrial matrix]
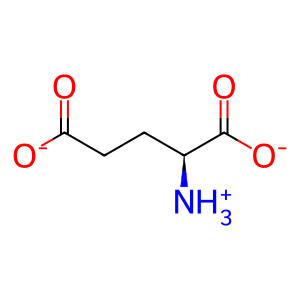
L-Glu [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-508179
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
L-glutamate(1-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
2-oxoglutarate(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-508179