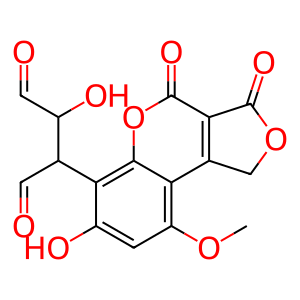
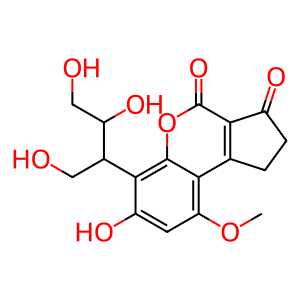
Reaction: AKR dimers reduce AFBDHO to AFBDOH
- in pathway: Aflatoxin activation and detoxification
Aflatoxin B1 aldehyde reductases (AKR7A2, AKR7A3 and AKR7L) are dimeric, cytosolic, NADPH-dependent enzymes able to catalyse the reduction of aflatoxin B1 dialdehyde (AFBDHO) to aflatoxin B1-6,8-dialcohol (AFBDOH) (Ellis et al. 2003, Bodreddigari et al. 2008, Ireland et al. 1998, Guengerich et al. 2001). AKRs can turnover a vast range of substrates, including drugs, carcinogens, and reactive aldehydes. They play central roles in the metabolism of these agents, leading to either their bioactivation or detoxication (Jin & Penning 2007). The dialcohol is excreted in urine by conjugation with glucuronide (not shown here).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
NADP+ [cytosol]
AFBDOH [cytosol]
AFBDHO [cytosol]
H+ [cytosol]
NADPH [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5423637
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
aflatoxin B1 dialdehyde
hydron
NADPH(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
NADP(3-)
aflatoxin B1 triol
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5423637