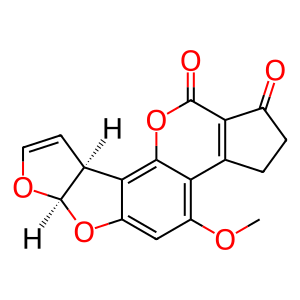
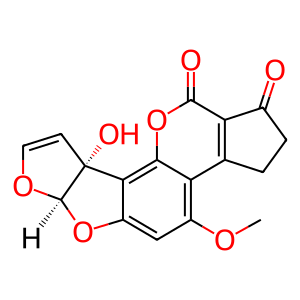
Reaction: CYP1A2 hydroxylates AFB1 to AFM1
- in pathway: Aflatoxin activation and detoxification
Aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) undergoes extensive oxidation, which is catalysed by cytochrome P450s. In addition to formation of the 8,9-oxide, oxidation by CYP1A2 yields a stable metabolite, aflatoxin M1 (AFM1), that is excreted in milk and urine (Ueng et al. 1995). AFM1 is less carcinogenic or mutagenic than AFB1, but is equally toxic.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
AFM1 [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
NADP+ [cytosol]
H+ [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
AFB1 [cytosol]
NADPH [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5423678
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
hydron
dioxygen
aflatoxin B1
NADPH(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
aflatoxin M1
water
NADP(3-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5423678