Reaction: Defective AHCY does not hydrolyse AdoHcy
- in pathway: Defective AHCY causes HMAHCHD
Adenosylhomocysteinase (AHCY) is a tetrameric, NAD+-bound, cytosolic protein that regulates all adenosylmethionine-(AdoMet) dependent transmethylations by hydrolysing the feedback inhibitor adenosylhomocysteine (AdoHcy) to homocysteine (HCYS) and adenosine (Ade-Rib) (Turner et al. 1998, Yang et al. 2003). Defects in AHCY cause Hypermethioninemia with S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase deficiency (HMAHCHD; MIM:613752), a metabolic disorder characterised by hypermethioninemia associated with failure to thrive, psychomotor retardation, facial dysmorphism with abnormal hair and teeth and myocardiopathy. Gene analysis revealed two mutations that can cause HMAHCHD; W112* and Y143C (Baric et al. 2004).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H2O [cytosol]
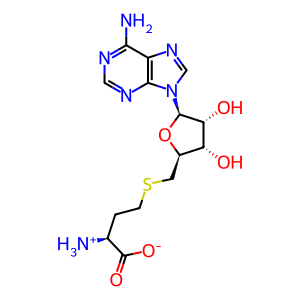
AdoHcy [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5579084
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine zwitterion
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5579084