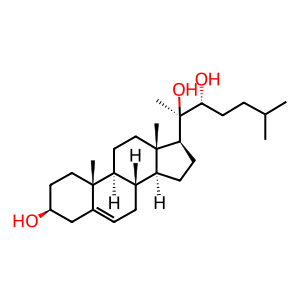
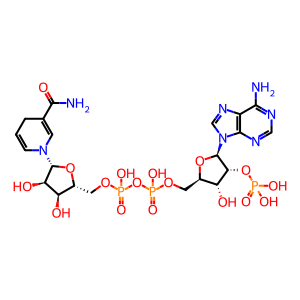
Reaction: Defective CYP11A1 does not cleave 20a,22b-DHCHOL
- in pathway: Defective CYP11A1 causes AICSR
Cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme, mitochondrial (CYP11A1) normally catalyses the side-chain cleavage of cholesterol to form pregnenolone. CYP11A1 is the active unit of a complex comprising adrenodoxin reductase (FDXR), adrenodoxin (FDX, or adrenodoxin-like protein FDX1L) (Strushkevich et al. 2011). Defects in CYP11A1 can cause Adrenal insufficiency, congenital, with 46,XY sex reversal (AICSR; MIM:613743). This is a rare disorder that can present as acute adrenal insufficiency in infancy with elevated ACTH and plasma renin activity and low or absent adrenal steroids. Although milder forms can present, associated with partial loss of enzyme activity, the severest phenotype is associated with prematurity, complete underandrogenisation and severe, early-onset adrenal failure. CYP11A1 mutations causing complete loss of function are a 6bp insertion resulting in the insertion of glycine and aspartate codons, a 1bp deletion resulting in a premature stop at 288 and the missense mutation V415E (Tajima et al. 2001, Hiort et al. 2005, Kim et al. 2008, Sahakitrungruang et al. 2010).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
O2 [mitochondrial matrix]
20a,22b-DHCHOL [mitochondrial inner membrane]
H+ [mitochondrial matrix]
NADPH [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5580269
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
dioxygen
(20R,22R)-20,22-dihydroxycholesterol
hydron
NADPH
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5580269