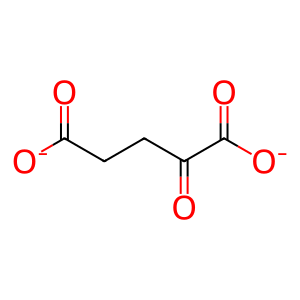
Reaction: OAT1-3 transport organic anions with antiport of dicarboxylic acids
- in pathway: Organic anion transport
The human gene SLC22A6 encodes organic anion transporter1 (OAT1). It was originally characterized in mouse as Novel Kidney Transcript (NKT). OAT1 is located on the basolateral membrane of the proximal tubule in human kidney as well as in the brain (Reid G et al, 1998; Lu R et al, 1999; Hosoyamada M et al, 1999). The human gene SLC22A7 encodes organic anion transporter 2 (OAT2) and is highly expressed in the liver and kidney (Sun W et al, 2001; Kobayashi Y et al, 2005). The human gene SLC22A8 encodes organic anion transporter 3 (OAT3) which is expressed mainly in the brain and kidney (Race JE et al, 1999; Bakhiya A et al, 2003).
OAT1-3 transport organic anions such as p-aminohippurate and drugs such as cimetidine and acyclovir. This transport is is coupled with an efflux of one molecule of endogenous dicarboxylic acid such as alpha-ketoglutarate (2-oxoglutarate). OAT2 is classified as both a transporter of organic anions and sulphate conjugates.
OAT1-3 transport organic anions such as p-aminohippurate and drugs such as cimetidine and acyclovir. This transport is is coupled with an efflux of one molecule of endogenous dicarboxylic acid such as alpha-ketoglutarate (2-oxoglutarate). OAT2 is classified as both a transporter of organic anions and sulphate conjugates.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
2OG [extracellular region]
2OG [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-561041
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
2-oxoglutarate(2-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
2-oxoglutarate(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-561041