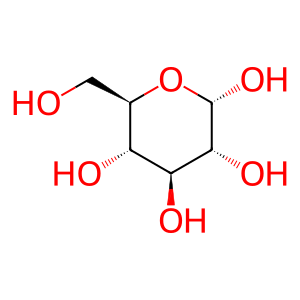
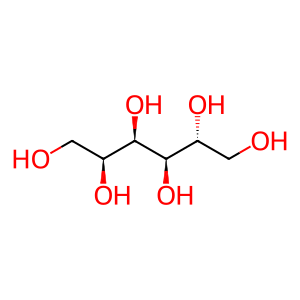
Reaction: AKR1B1 reduces Glc to D-sorbitol
- in pathway: Fructose biosynthesis
Cytosolic AKR1B1 (aldose reductase) catalyzes the reaction of glucose (Glc) and NADPH + H+ to form D-sorbitol and NADP+. This reaction was first described by Hers (1960) in sheep seminal vesicles; the human enzyme was identified by Nishimura et al. (1990) and is a potential target for treatment of diabetic neuropathy (Oates, 2008). The active enzyme is a monomer (Ruiz et al. 2004) whose amino-terminal methionine residue has been removed (Jacquinod et al. 1993). Under physiological conditions, formation of D-sorbitol is strongly favored (Grimshaw 1992).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
NADP+ [cytosol]
D-sorbitol [cytosol]
H+ [cytosol]
NADPH [cytosol]
Glc [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5652172
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
hydron
NADPH(4-)
alpha-D-glucose
Reaction output - small molecules:
NADP(3-)
D-glucitol
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5652172