Reaction: AGMO cleaves alkylglycerol into fatty aldehyde and glycerol
- in pathway: Triglyceride biosynthesis
Ether lipids (alkylglycerols, glyceryl ethers) are essential components of brain membranes, protect the eye from cataract, mediate signalling processes and are required for spermatogenesis. Alkylglycerol monooxygenase (AGMO) is a tetrahydrobiopterin-dependent protein and is the only enzyme known to cleave the ether bond of alkylglycerols and lyso-alkylglycerol phospholipids into fatty aldehydes and glycerol derivatives (Watschinger et al. 2010).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H2O [cytosol]
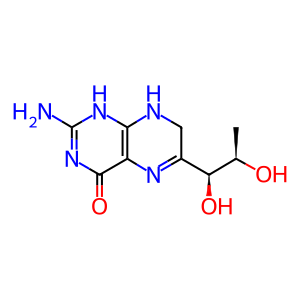
BH2 [cytosol]
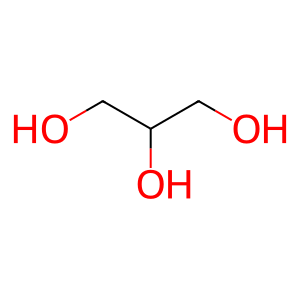
Glycerol [cytosol]
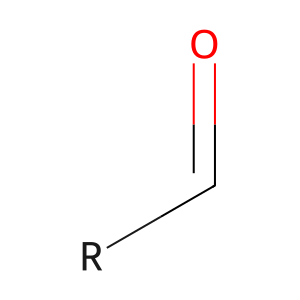
fatty aldehyde [cytosol]
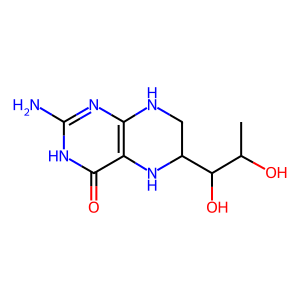
BH4 [cytosol]
alkylglycerol [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5696119
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobiopterin
alkylglycerol
dioxygen
Reaction output - small molecules:
water
D-erythro-7,8-dihydrobiopterin
glycerol
fatty aldehyde
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5696119