Reaction: AKR1B15 reduces EST17b to E1
- in pathway: Estrogen biosynthesis
The aldo-keto reductases (AKRs) are multifunctional enzymes that catalyse the reduction of biogenic and xenobiotic aldehydes and ketones as well as the synthesis and metabolism of sex hormones. The newest identified member, Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B15 (AKR1B15) is able to catalyse the reduction of 17beta-sex hormones such as 17beta-estradiol (EST17b) to estrone (E1). Two isoforms of AKR1B15 exist in different subcellular locations; isoform 2 is cytosolic (like most AKRs) whereas isoform 1 co-localises with the mitochondria (Weber et al. 2015).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [mitochondrial matrix]
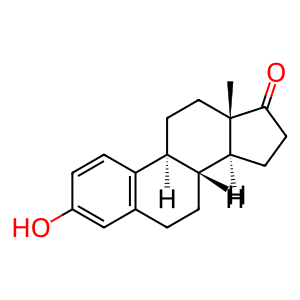
E1 [mitochondrial matrix]
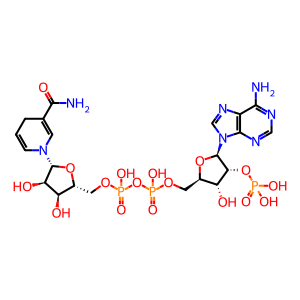
NADPH [mitochondrial matrix]
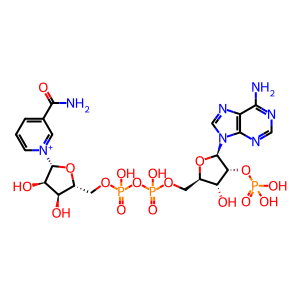
NADP+ [mitochondrial matrix]
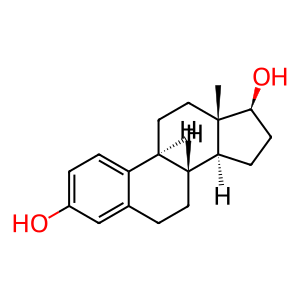
EST17b [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-5696822
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
NADP(+)
17beta-estradiol
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
estrone
NADPH
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-5696822