Reaction: LIAS:2(4Fe-4S) transforms octanoyl-K107-GCSH to lipoyl-K107-GCSH
- in pathway: Glyoxylate metabolism and glycine degradation
Lipoate is an essential cofactor for five redox reactions; four in oxoacid dehydrogenases (active in energy metabolism and amino acid metabolism) and one in the glycine cleavage system (GCS). Lipoate synthesis in mitochondria requires three steps. In the second step, mitochondrial lipoyl synthase (LIAS) mediates the radical-mediated insertion of two sulfur atoms into the C-6 and C-8 positions of the octanoyl moiety bound to glycine cleavage system H protein (GCSH), transforming the octanoyl moiety to a lipoyl moiety. LIAS requires two 4Fe-4S clusters as cofactor which act as the sulfur donors in the reaction (Morikawa et al. 2001). Defects in LIAS causes neonatal-onset epilepsy, defective mitochondrial energy metabolism, and glycine elevation (Mayr et al. 2011).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
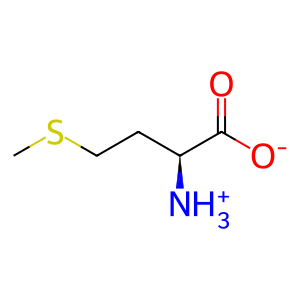
L-Met [mitochondrial matrix]
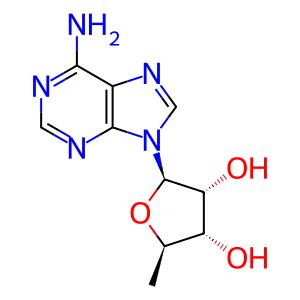
5dAde [mitochondrial matrix]
S [mitochondrial matrix]
AdoMet [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-6793591
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
sulfur atom
S-adenosyl-L-methionine
Reaction output - small molecules:
L-methionine zwitterion
5'-deoxyadenosine
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-6793591