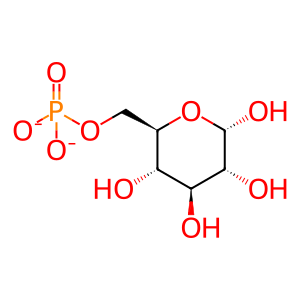
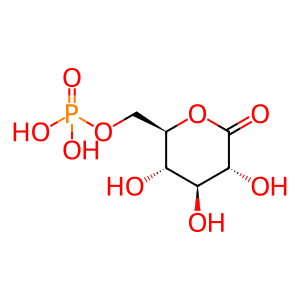
Reaction: alpha-D-glucose 6-phosphate + NADP+ => D-glucono-1,5-lactone 6-phosphate + NADPH + H+
- in pathway: TP53 Regulates Metabolic Genes
Cytosolic glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) catalyzes the reaction of glucose 6-phosphate and NADP+ to form D-glucono-1,5-lactone 6-phosphate and NADPH + H+. This constitutes the first committed step of the pentose phosphate pathway and it is critical to the maintenance of NAPDH pool and redox homeostasis. For this reason, anti-cancer therapies are making this step as a prominent target in cancer therapy (Zhang et al. 2014). The reaction is inhibited by high ADP/AMP concentration, and by high NAPDH concentration. Biochemical studies indicate that both G6PD dimers and tetramers are catalytically active and present under physiological conditions in vivo (Au et al. 2000). Mutations that reduce the catalytic efficiency of G6PD are remarkably common in human populations; these appear to have a protective effect against malaria (e.g., Luzzatto and Afolayan 1968).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [cytosol]
D-Glucono-1,5-lactone 6-phosphate [cytosol]
NADPH [cytosol]
G6P [cytosol]
NADP+ [cytosol]
H+ [cytosol]
D-Glucono-1,5-lactone 6-phosphate [cytosol]
NADPH [cytosol]
G6P [cytosol]
NADP+ [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-70377
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
alpha-D-glucose 6-phosphate(2-)
NADP(3-)
alpha-D-glucose 6-phosphate(2-)
NADP(3-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
6-O-phosphono-D-glucono-1,5-lactone
NADPH(4-)
hydron
6-O-phosphono-D-glucono-1,5-lactone
NADPH(4-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-70377