Reaction: PXLP-K314-GPT transaminates L-Ala to form PYR
- in pathway: Alanine metabolism
Cytosolic glutamic-pyruvate transaminase (alanine aminotransferase) (GPT) catalyzes the reversible reaction of alanine and 2-oxoglutarate (alpha-ketoglutarate) to form pyruvate and glutamate (Sohocki et al. 1997; Yang et al. 2002). The active form of the enzyme is a dimer (Ishiguro et al. 1991) and is inferred to have a molecule of pyridoxal phosphate associated with each monomer. This reaction allows the synthesis of alanine from intermediates of glucose metabolism in a well-fed person. Under fasting conditions, alanine, derived from protein breakdown, can be converted to pyruvate and used to synthesize glucose via the gluconeogenic pathway in liver, or fully oxidized via the TCA cycle in other tissues.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
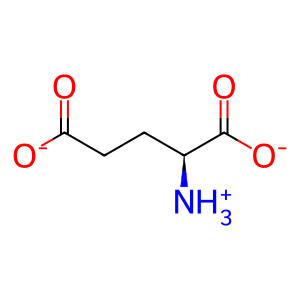
L-Glu [cytosol]
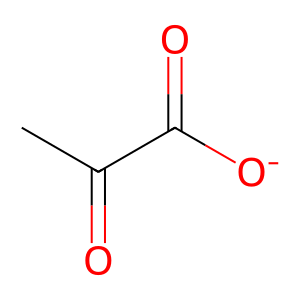
PYR [cytosol]
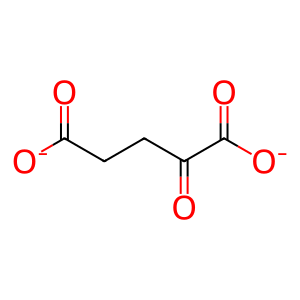
2OG [cytosol]
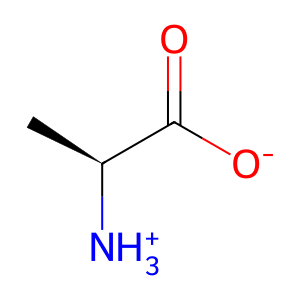
L-Ala [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-70523
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
2-oxoglutarate(2-)
L-alanine zwitterion
Reaction output - small molecules:
L-glutamate(1-)
pyruvate
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-70523