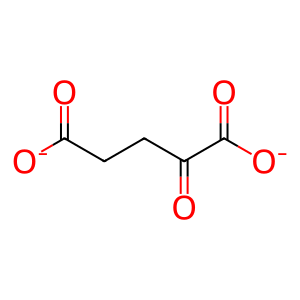
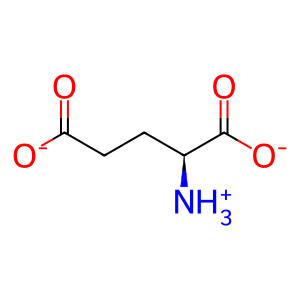
Reaction: alpha-ketoglutarate + NH4+ + NAD(P)H + H+ <=> glutamate + NAD(P)+ [GLUD1]
- in pathway: Glutamate and glutamine metabolism
Mitochondrial glutamate dehydrogenase 1 (GLUD1) catalyzes the reversible reaction of 2-oxoglutarate, NAD(P)H + H+, and ammonia to form glutamate and NAD(P)+ (Fang et al. 2002). Mature GLUD1 protein lacks the 53 aminoterminal residues of the nascent protein (Julliard and Smith 1979), which function as a mitochondrial import signal. The active form of the enzyme is a hexamer, allosterically activated by ADP and inhibited by GTP (Fang et al. 2002; Smith et al. 2002).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
L-Glu [mitochondrial matrix]
H2O [mitochondrial matrix]
2OG [mitochondrial matrix]
H+ [mitochondrial matrix]
NH4+ [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-70589
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
2-oxoglutarate(2-)
hydron
ammonium
Reaction output - small molecules:
L-glutamate(1-)
water
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-70589