Reaction: GOT2 transaminates oxaloacetate and glutamate
- in pathway: Gluconeogenesis
Mitochondrial GOT2 (glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase 2, also known as aspartate aminotransferase, mitochondrial) catalyzes the reversible transamination of oxaloacetate (OA) and glutamate (L-Glu) to form aspartate (L-Asp) and 2-oxoglutarate (2-OG, alpha-ketoglutarate) (Martini et al. 1985; van Karnebeek et al. 2019). The active form of the enzyme is a homodimer of GOT2 monomers each conjugated with pyridoxal phosphate on lysine residue 279.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
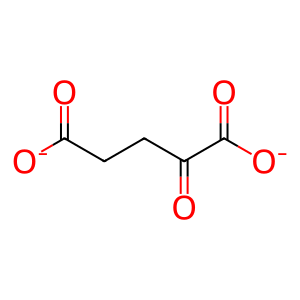
2OG [mitochondrial matrix]
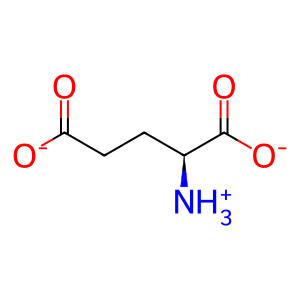
L-Asp [mitochondrial matrix]
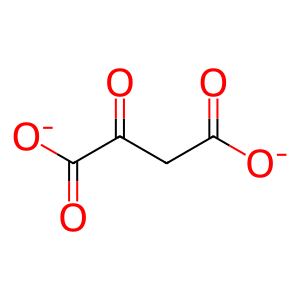
OA [mitochondrial matrix]
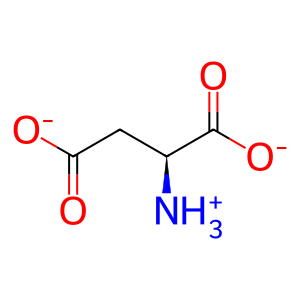
L-Glu [mitochondrial matrix]
2OG [mitochondrial matrix]
L-Asp [mitochondrial matrix]
OA [mitochondrial matrix]
L-Glu [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-70613
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
oxaloacetate(2-)
L-glutamate(1-)
oxaloacetate(2-)
L-glutamate(1-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
2-oxoglutarate(2-)
L-aspartate(1-)
2-oxoglutarate(2-)
L-aspartate(1-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-70613